Invasion and Migration
BioTest4U has experience with specialized assays analyzing the single-cell migration (SCM) and collective-cell migration (CCM) in vitro as well as tumor invasion in vivo.
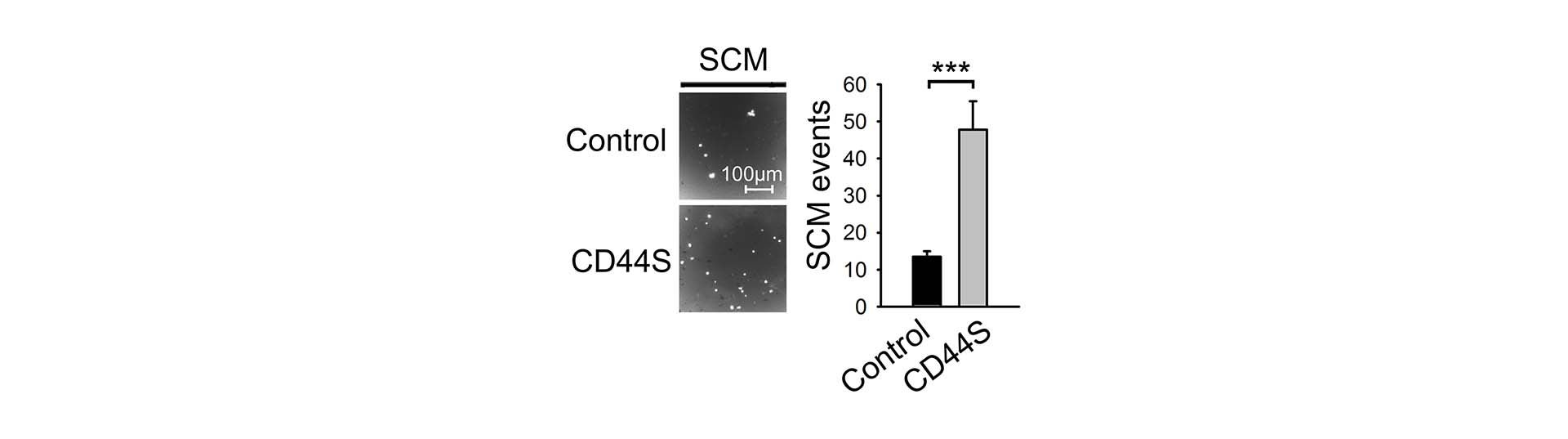
Single-cell migration (SCM) through cell culture inserts with defined pore size of cells expressing normal level of CD44 and of their more tumorigenic counterparts that overexpress the standard isoform of CD44 (CD44S).
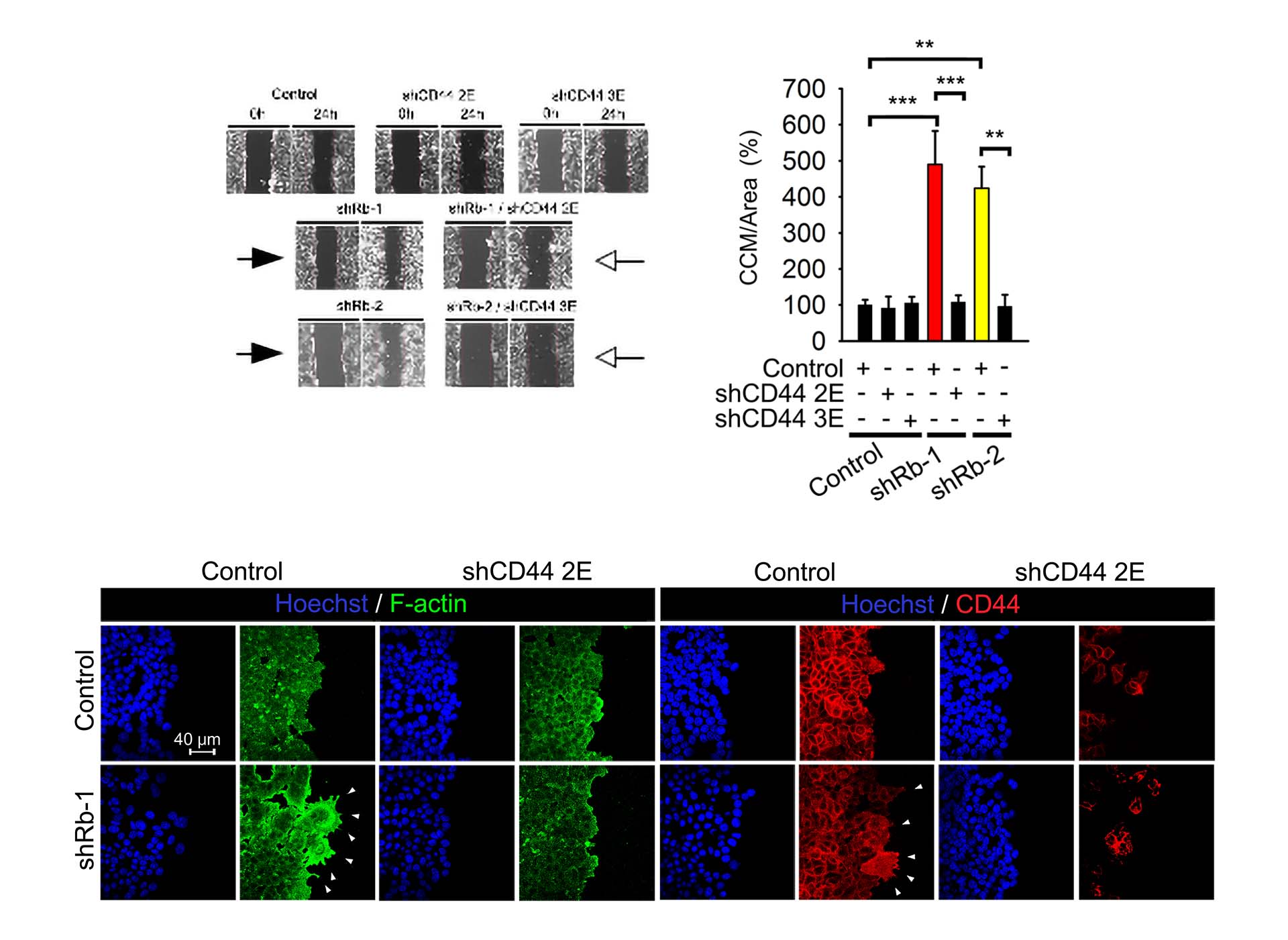
Collective cell migration (CCM) assays monitor the migration of cells into a pre-configured empty “scratch” region on the culture vessel. Image (left) shows the treatments that enhance migration and narrow the empty region. Reported migration calculation is performed using image analysis software.
In this study, knockdown of Rb by Rb-1 or Rb-2 shRNA increased CCM (filled arrows). The enhancing effect on CCM was lost by delivery of shRNA against isoforms of CD44 (open arrows). The CCM assay is readily quantified (chart, right).
The results from CCM were further analyzed by immunostaining (bottom panel), that reveals how morphology of the lead migration end can change in pro-tumorigenic conditions.

In vivo invasion assay. Detection of in vivo invasion in an assay with fluorescently labelled cell lines. Invasion into mammary fat pad (MFP) or lymphovascular regions is clearly visible in high resolution images of sub-regions 1-4. This in vivo study produced data consistent with the findings of the CCM assay above, wherein knockdown of Rb using shRNAs increased invasion in a mannerthat also required the presence of CD44 isoforms.



