Circulating Tumor Cells
We can detect, analyze and isolate circulating tumor cells from mouse models and patient samples. We detect all types of carcinoma cells, cell clusters and cell ghosts (nuclei-free particles with cell membrane/cytoskeleton) that are present in the white-blood cell fraction using flow cytometry, flow sorting and microscopy.
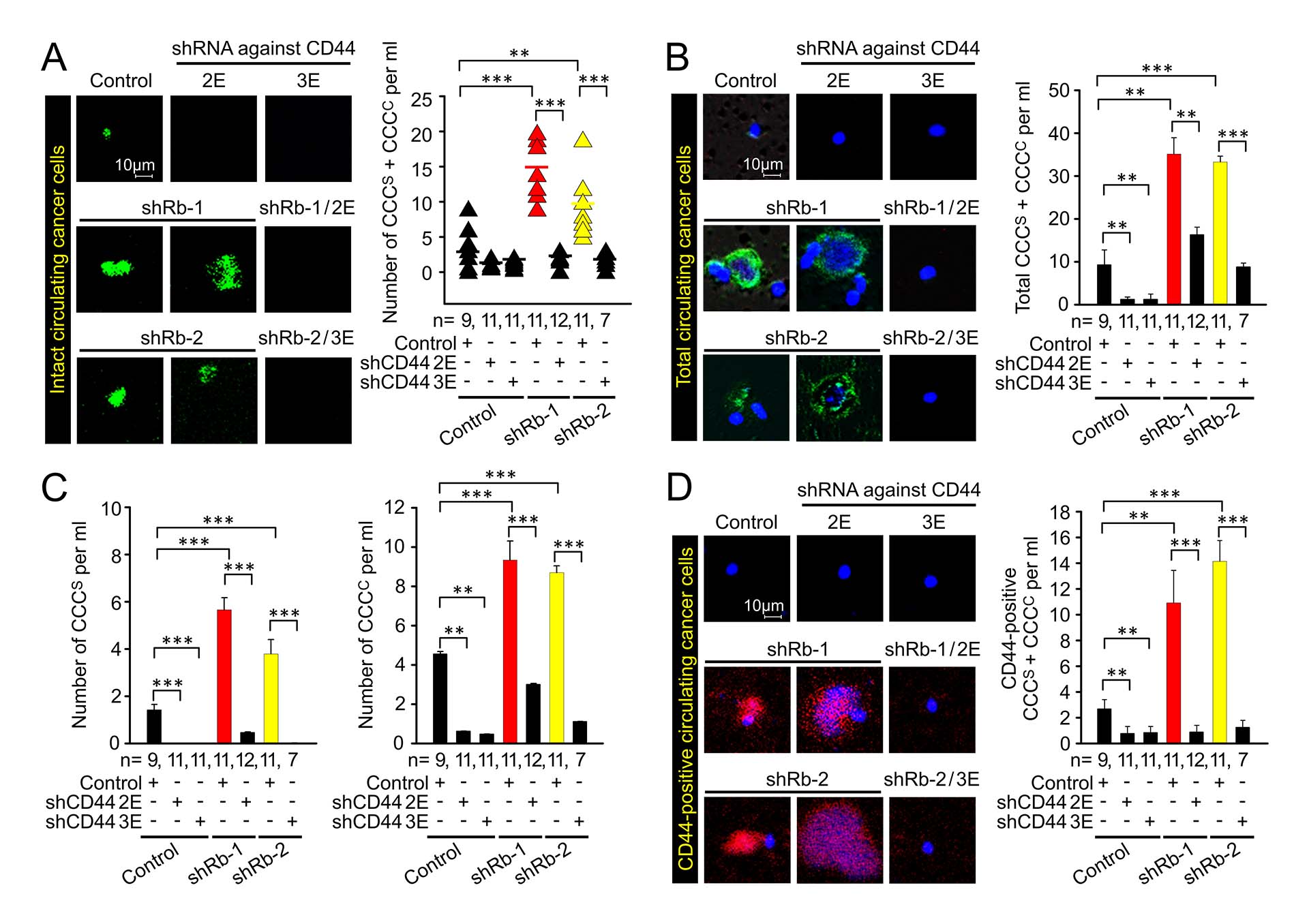
Fluorescence images and quantification of circulating live cancer cells and cell clusters co-isolated with mononuclear fraction from blood of animals bearing tumors. The tumors were induced by orthotopic implantation of MCF7ras cells expressing shRNAs against Rb, CD44, and their combination, along with respective controls. EGFP is expressed in the cytoplasm and its presence indicates both cancer cell identity and presumably intact membrane. (A) circulating tumors cells expressing endogenously expressed EGFP, (B) circulating tumor cells expressing epithelial marker, (C) Quantification of circulating single cancer cells (CCCs) and circulating tumor cell clusters (CCCc) from (B), (D) detection and quantification of circulating tumor cells expressing CD44.
As with other studies on our website, the data support a role for Rb in restricting all stages of metastatic progression. In this study, knockdown of Rb increased the number of circulating tumor cells. This effect required the presence of CD44 isoforms, as shown by reduced levels of circulating tumor cells in animals whose tumors were induced by Rb-knockdown cells that were treated with shRNAs against CD44 isoforms.


